
All-In-One Scriptless Test Automation Solution!
All-In-One Scriptless Test Automation Solution!
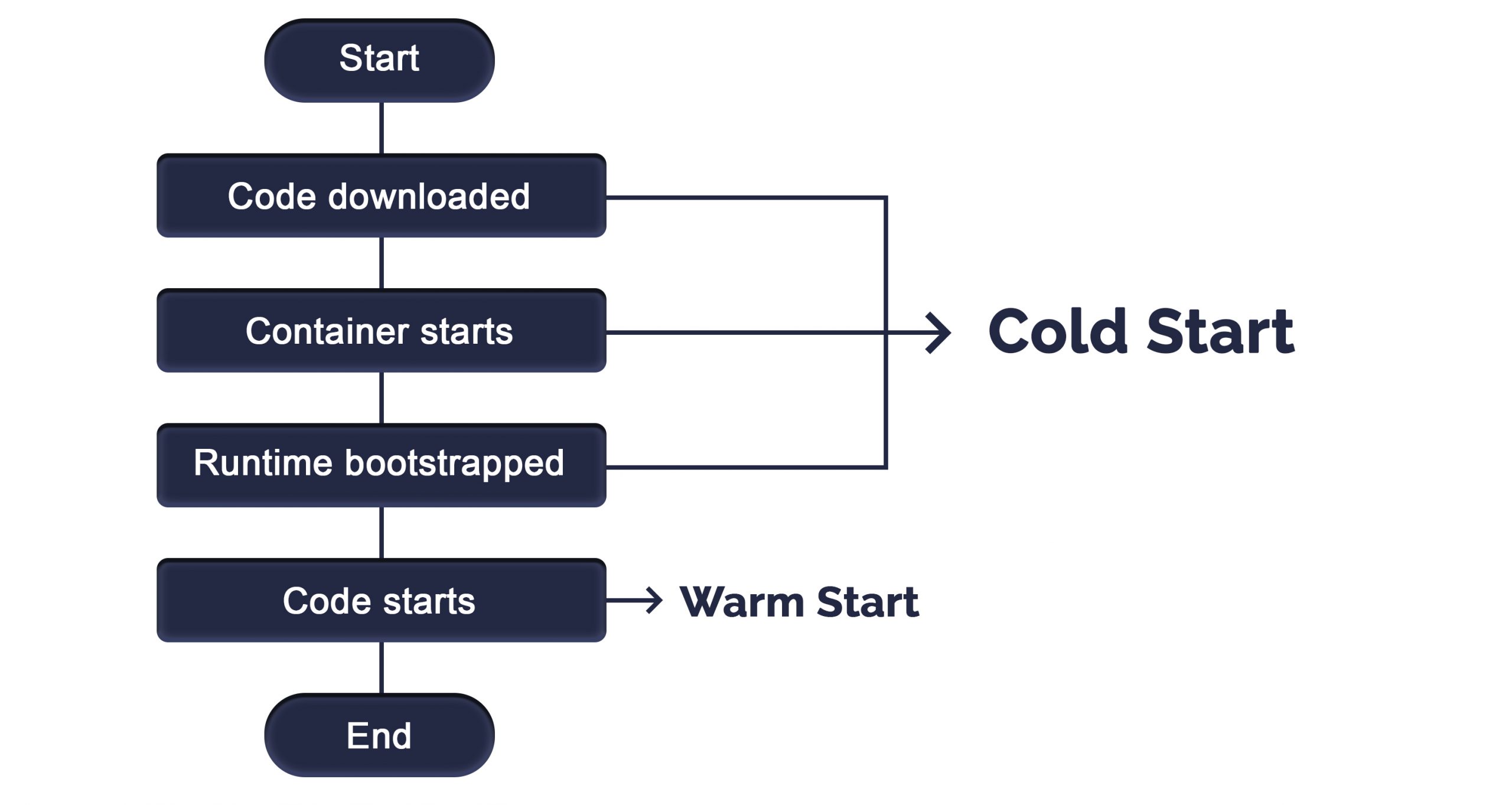
Serverless is a cloud computing deployment model to execute applications by running functions on-demand. The main advantage of serverless is that it allows an application, or part of an application, to be deployed in whenever required. It does not require an always running execution environment. serverless computing is an execution strategy for the cloud. A cloud provider may be google cloud or Aws or Azure, dynamically allocating and charging the user for—only the compute resources and storage required to deploy a specific piece of code.
Thus, serverless execution models can help to save money. Instead of maintaining a server 24/7, companies can deploy code in a serverless environment and pay only for the consumed resources.
Some of the brand cloud migration consulting providers of IT help in the form of cloud services are Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, etc. Undeniably, there are other best-quality companies in this escalating international mix, with names such as Salesforce, Alibaba, Rackspace, TenCent, Equinix, Oracle, Dell EMC, and other Tier 2 and 3 players. But just because these companies are not in the top four doesn’t mean they won’t be the right choice for your business. Smaller and more professional is what many organizations prefer and search out.
This article will explore three of the top four at a high business level. The effect of the Big 3 in the market, think of them in this prospect:
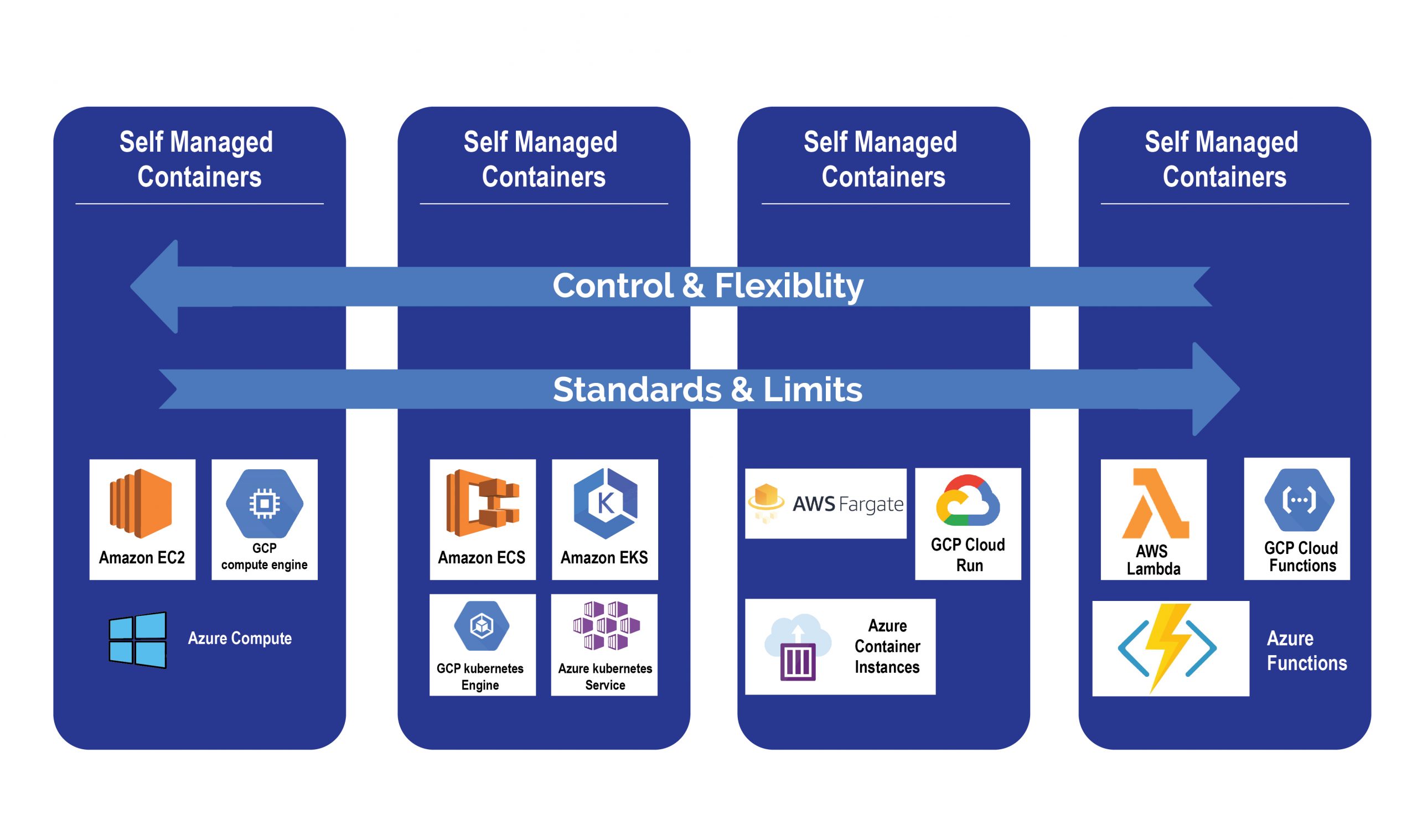
The most crucial factor you have to examine when running container workloads on cloud providers is whether you need to use managed services or commodity services (“do it yourself”).
“Do It Yourself” gives you more control over your container environment’s abilities. The typical cloud services can save time in maintaining the systems, as they are centrally managed and more stable. Altogether using managed services to run container workloads can free up your engineering resources to focus on higher-value work.
There are various options within managed services, such as how much of the infrastructure management you need to control and how much you want the cloud providers to take on for you. Usually, the trade-off is between cost, convenience, and control.
Kubernetes plays a prominent role in the container function space, and all three principal providers deliver a managed Kubernetes service. Initially, it was Google Cloud with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) in 2014, followed by Azure with Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) in 2017, and ultimately AWS followed with Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) in 2018. While there are dissimilarities in their details, all of these services are broadly alike in their general contribution.
Each cloud provider also provides a registry service to build and store your container images. Google has Google Container Registry (GCR), Amazon has Elastic Container Registry (ECR), Azure has Azure Container Registry (ACR).
The cloud service platform from Amazon is Amazon Web Services (AWS), which offers services in various domains that include storage, compute, delivery, and other functionalities. AWS helps enterprises to scale and grow. AWS uses these domains in the form of services that can be used to deploy various types of applications in the cloud platform. These services work with each other and yield a productive and scalable result. AWS services are divided into three types:
Amazon launched AWS in 2006. It is the most-purchased cloud platform among existing available cloud platforms. Cloud platforms provide many advantages such as cost minimization, management overhead reduction, and many others.
Azure provides a set of container services that is similar to AWS. AWS Fargate and ECS are Azure Container Instances (ACI), an alternate clustering solution for containerized workloads. The main difference between AWS ECS and ACI is that ACI is sketched from the ground up to run on servers managed by Azure rather than by the users themselves. Ultimately, Azure’s equal to App Mesh is Azure Service Fabric.
Azure is designed and built by Microsoft and launched in 2010. It competes directly with AWS by offering services in domains that include database, developer tools, compute, storage, networking, and other functionality, enabling enterprises to grow their businesses.
Azure services are classified as:
They all can be used by software employees and developers to create, manage, deploy services and applications through the cloud.
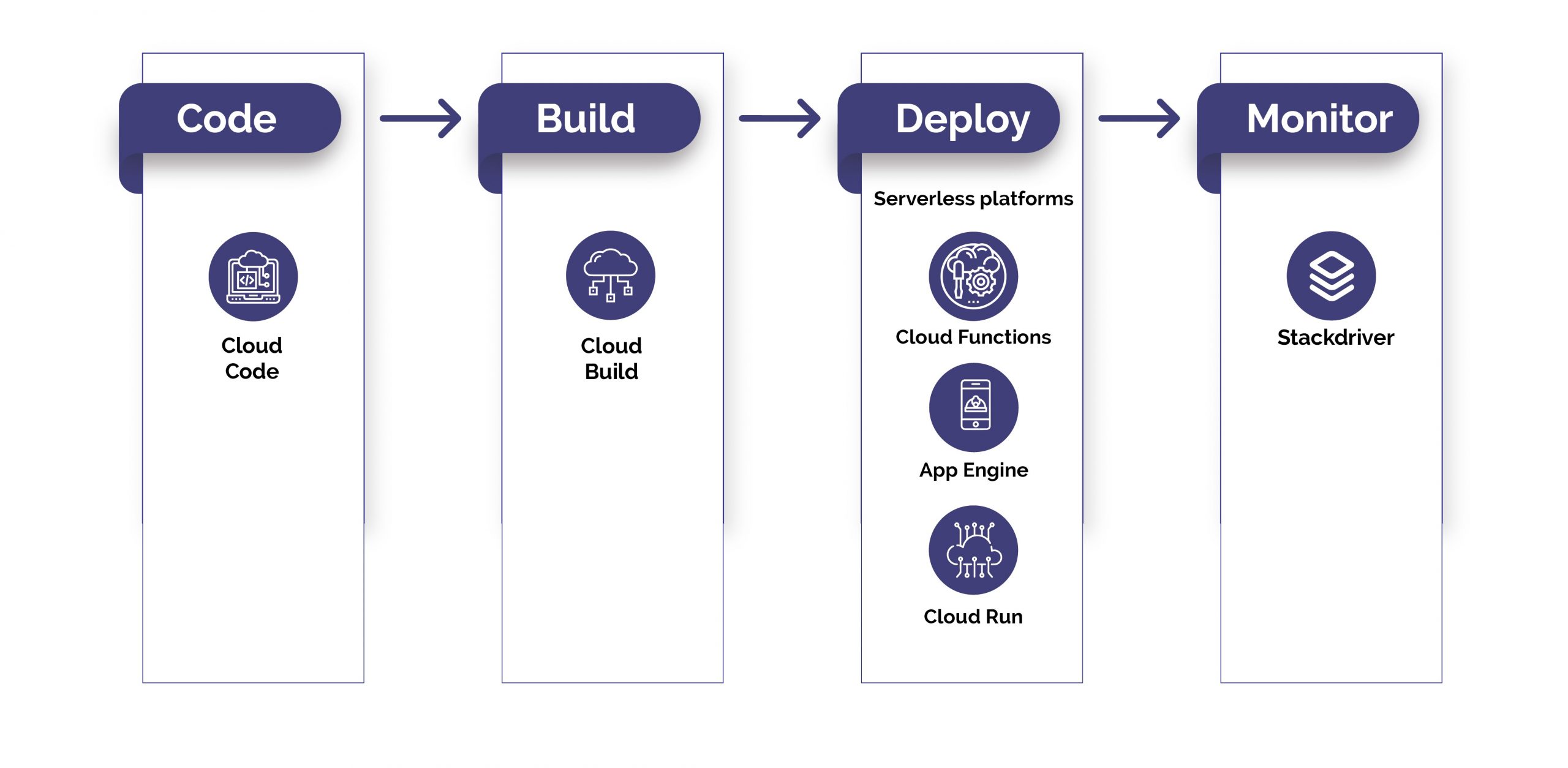
Google Cloud is a cloud computing platform. It was developed by Google and launched in 2008 and written in C++, Java, Python, including Ruby. It also offers various services that are IaaS, PaaS, and Serverless platform. Google cloud is classified into different platforms, such as Google Compute Engine, Google Cloud Datastore, Google Big Query, Google Cloud SQL, Google App Engine, and Google Cloud Storage. Google cloud platform offers high-level computing, networking, storage, and databases. It also provides different networking options, such as cloud CDN, virtual private cloud, cloud DNS, load balancing, and other additional features.
Even before Google Cloud emerged, Google was an innovator in container-based services and even containers themselves: Google engineers were incorporated into the introduction of containers to the Linux kernel by introducing groups back in 2006.


Vaidy is an experienced lead Solutions Architect heading sales and project delivery for Cloud (AWS, Azure), DevOps and legacy Modernization projects with a demonstrated history of working in the information technology and services industry. He is a strong engineering professional with a Master of Science (MS) focused in Computer Software Engineering from BITS Pilani. He has the capability to manage bigger teams and generate revenue through new Sales and Account Mining.
Get everything you require from best practices and guidelines to secure your cloud platforms today. Talk to us!
One reply on “Run Serverless containers on AWS / GCP / Azure”
Enterprises increasingly are seeing the cloud as a digital transformation engine as well as a technology that improves business continuity. As work was forced to go remote due to stay-at-home orders, tasks were largely done on cloud infrastructure.